Hostwinds Tutorials
Search results for:
Table of Contents
My Server is Not Working Correctly – What Should I Do?
Tags: WHMCS
If you find that your server instance is not working as expected, there are a few things that you can do to troubleshoot the cause. The steps required to troubleshoot this will vary depending on what OS you have installed and the issue that you're experiencing with the server. This article will cover the required steps for a Linux-based server with cPanel. However, some of these steps can be utilized on a Linux server without cPanel.
Top Command
The first thing that you can do is log in to your server via SSH and check the output of the top command. The top is a command-line utility that can be used to check the load of your server. To check top, issue the following command via SSH.
top
You should see output similar to the following:
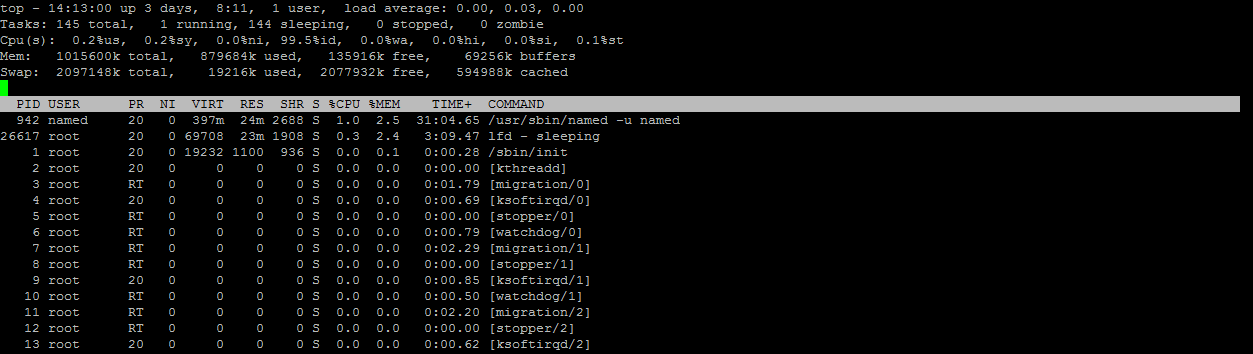
The load is generally displayed in the upper right-hand corner, as you can see in the image below:
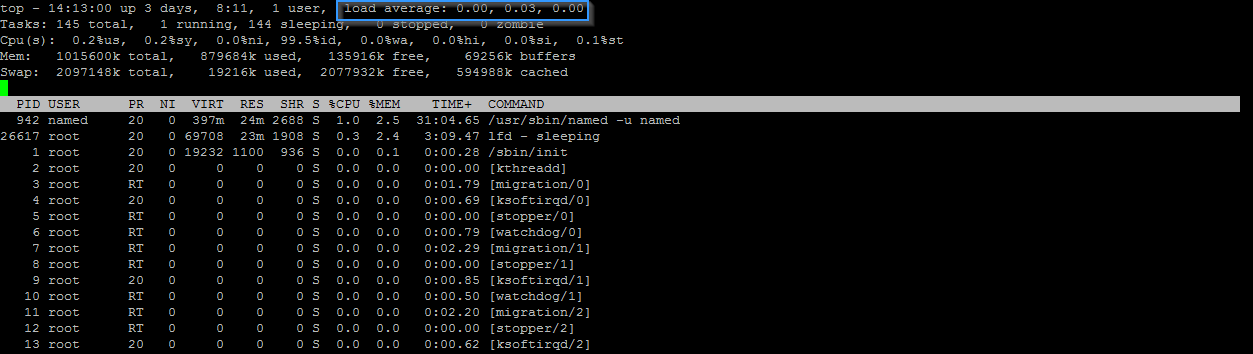
The resources of the server instance will ultimately determine what type of load is acceptable. However, if you see a load higher than 10 and the server performs slowly, you'll need to investigate further what is causing the load.
Process Manager (WHM)
If you have WHM, you can check the server's load simply by logging in, as the load is generally displayed on the main page.

For a more in-depth look at each process and its resource usage, you can use the Process Manager in WHM.
- Search for "process" in the search bar
- Select Process Manager under System Health
With the Process Manager, you can Kill processes or trace them and get an idea of the resource utilization of each process.
Check Apache
The next step is to check the Apache webserver to see if it is running. This can be done a few ways depending on your OS and if you're using cPanel. Let's take a look at a few common ways to check if Apache is running.
CentOS 6
You can check if Apache is running in CentOS 6 by issuing the following command while logged in via SSH:
service httpd status
If this command returns that Apache is stopped, you can start it using this command:
service httpd start
You can also restart Apache at any time by using the following:
service httpd restart
CentOS 7
To check Apache's status in CentOS 7, please issue the following command:
systemctl status httpd
If the output of this command states that Apache is stopped, you can start it by issuing this command:
systemctl start httpd
You can also restart the Apache webserver via this command:
systemctl restart httpd
WHM
You can check Apache's status by utilizing the steps below. Please note that you'll need to be logged into WHM before continuing.
- Search for "apache" in the search bar
- Select Apache Status under the Server Status section
You can also restart Apache from within WHM.
- Search for "apache" in the search bar
- Select HTTP Server (Apache) under the Restart Services section
- Select Yes
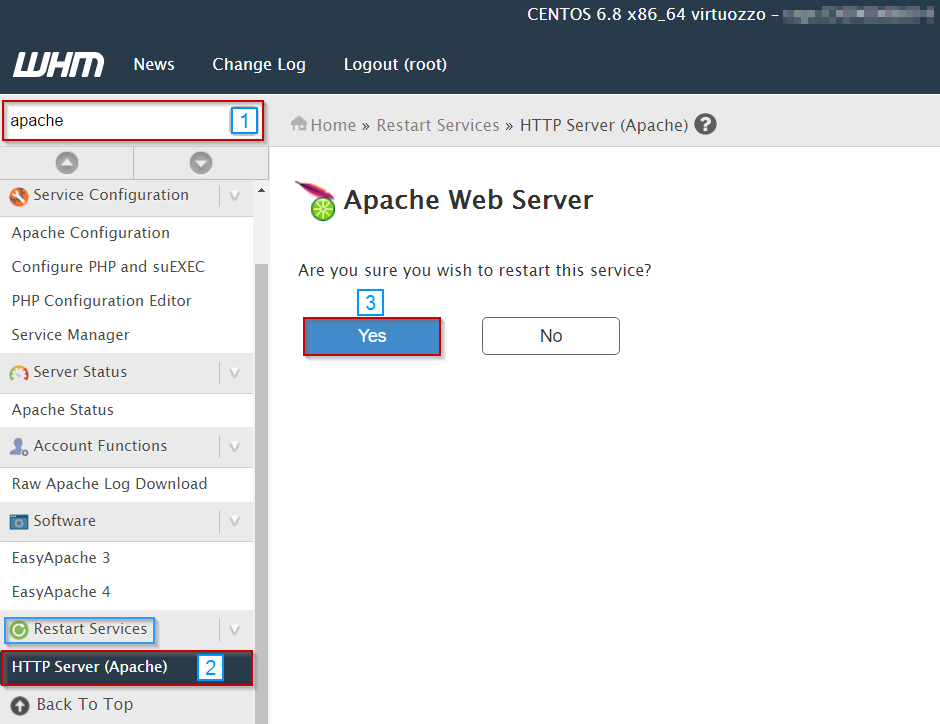
Apache should now be restarting.
Reboot the server
In some cases, you just need to reboot the server. As the adage states, "have you tried turning it off and back on again?" can hold very true. Rebooting the server can be accomplished in a few ways; via SSH, WHM (if purchased), and through the Hostwinds client area.
SSH
To reboot the server via SSH, you'll first need to be logged in to the server as the root user through SSH. Once logged in as root, issue the following command:
reboot -h now
Or
shutdown -h now
Either command should suffice to reboot the server gracefully.
WHM
To reboot the cloud instance using WHM, you'll first need to log in to WHM.
- Search for "reboot" in the search bar
- Select Graceful Server Reboot
- Click Proceed
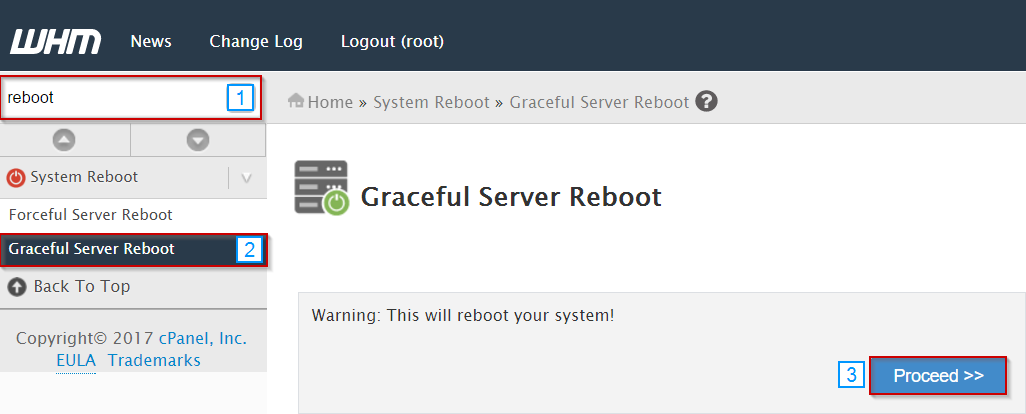
The server should now be rebooting.
Hostwinds Client Area
First, you'll need to log in to the Hostwinds client area to proceed.
- Log in to your Client Area
- Select Cloud Control >> Cloud Portal
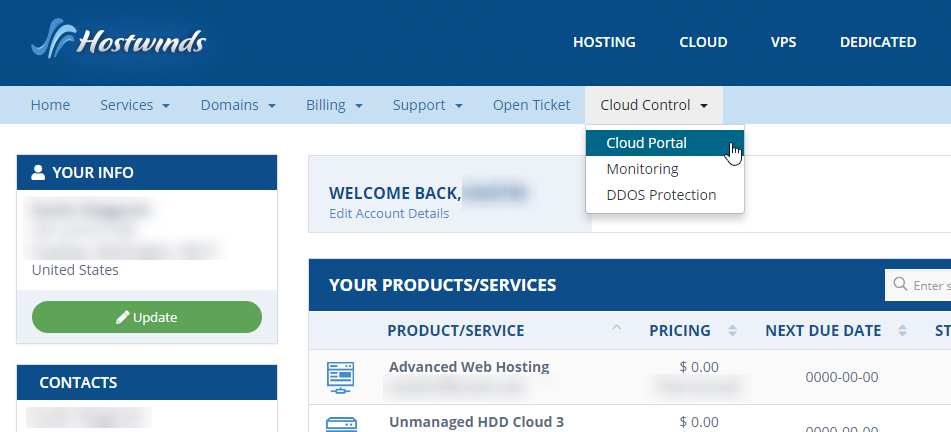
- This will take you into your Cloud Portal. You can select the Reboot option from the Actions dropdown next to the server you wish to reboot from here.
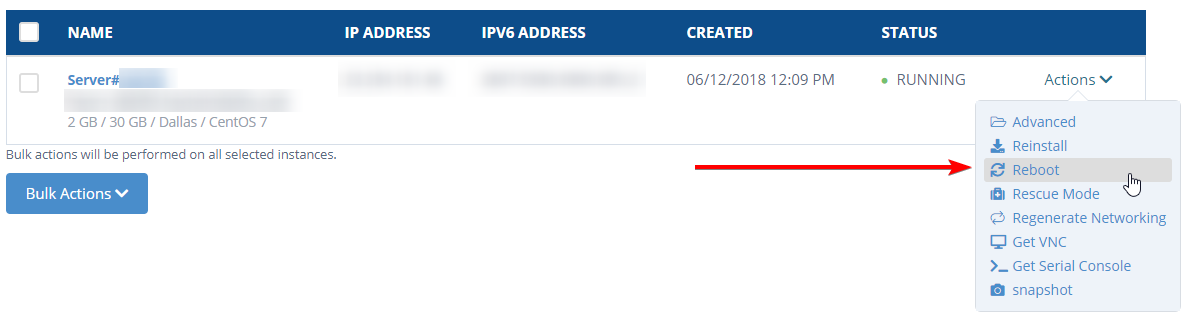
Note: If you have an older VPS, you will need to select Services >> My Services from your Client Area home page and selecting "Manage" next to the server you wish to reboot. Once you scroll down, you'll notice a Reboot option that you can select.
The server should now be rebooting.
If the server is still experiencing issues, please feel free to contact us by Opening a Support Ticket so that we may take a closer look for you.
Written by Michael Brower / June 23, 2017
