Hostwinds Tutorials
Search results for:
Table of Contents
DNS Servers, Roles and Functions
Tags: DNS
The internet is a confusing web of connections, protocols, servers, service providers, and more. However, there are many interconnecting forces at work that help your browser provide the content you expect. Domain name services, or DNS, is a large part of what helps this remain consistent. This guide aims to help you understand DNS roles and functions.
Domain Name Services
The internet is a network of connected computers either publicly available or within a private, internal network. These computers and resources are all assigned an IP address. For instance, Google's home page is hosted on one of many different IP addresses. So how does your browser know, then, to go to those IP addresses when all you give it is a domain name? That is where DNS comes into play. DNS associates a domain name to a place to find content for that domain.
The Roles of DNS
When you want to call someone, you typically load up your contact list, tap their name, and hit call. You know that behind the scenes, this associates a phone number with the contact, and your cellular connection initiates a phone call. DNS is your internet phonebook. It lets you tell your browser to fetch a domain name and automatically know the physical IP address, without you ever having to do more than hit the enter key and wait. Let's talk about this in more detail.
DNS Function
DNS relies on two major parts: a nameserver and DNS records. The purpose of a nameserver is to explicitly store information on how to find the DNS records. When your browser makes its request for a domain, the nameserver it uses provides a location to find details about the DNS records. Without too much detail, a DNS record is what actually converts a URL into an IP address.
Let's take a look at the below example. First, you enter google.com into your browser. Next, your browser reaches out to the root nameservers for any .com domain names from Verisign (the root) and finds the nameserver for google.com. That nameserver is ns1.google.com. Now, that nameserver points you to the DNS manager for the domain, google.com. Upon checking, the DNS manager provides 172.217.9.238 as the DNS record for google.com. Your browser then lands at the above IP address showing google.com's site content. A visual example of this process follows.
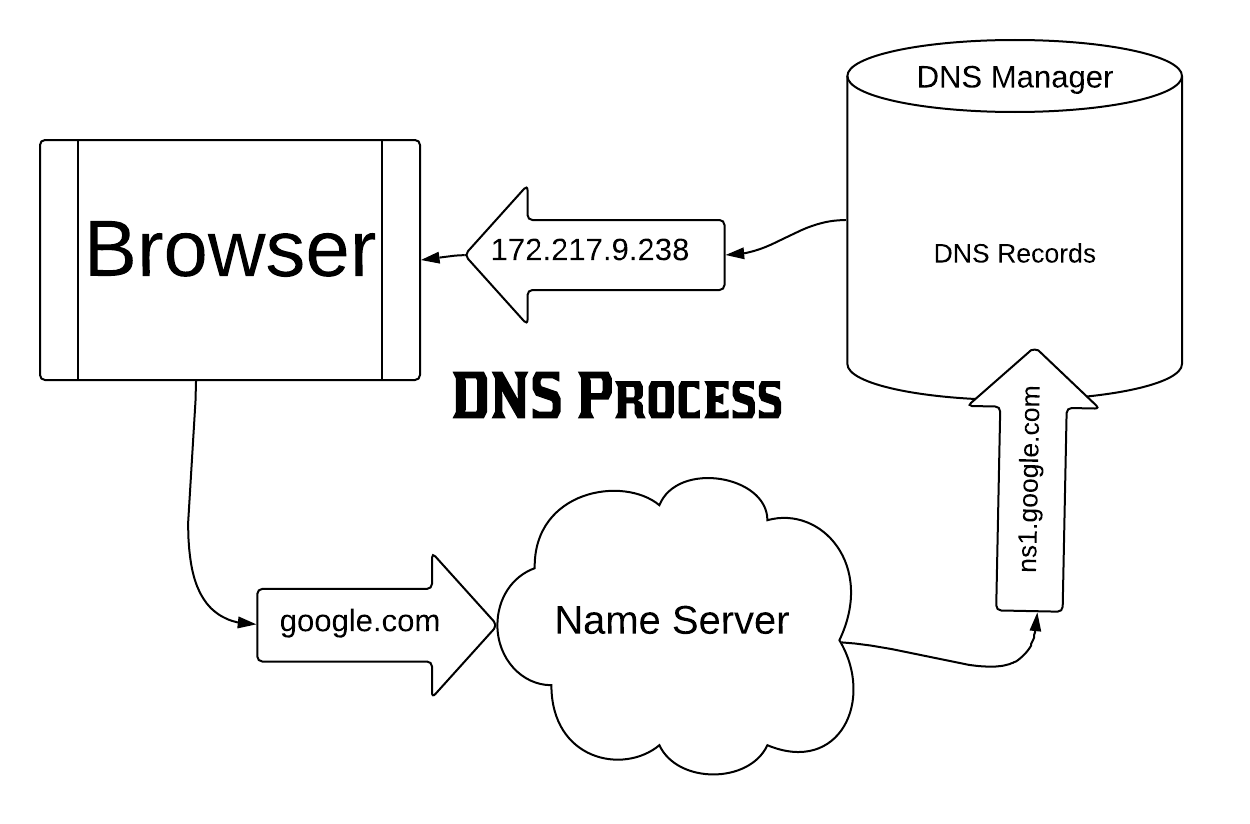
Example DNS Process
It can be a bit overwhelming, as it is a lot of information. However, even this is a fairly simple showcase of how DNS works. The most important takeaway here is that DNS is a crucial aspect of ensuring that the internet functions properly.
DNS at Hostwinds
Hostwinds offers options to manage DNS records for purchased domains or for DNS records that need to be managed in your Hostwinds Cloud Portal to point to your server. The nameservers we provide with your service control where your DNS records are managed. Let's provide a couple of example scenarios next.
Shared Web Hosting DNS
Within our Shared Web Hosting plans, your DNS records are managed by your cPanel account. To allow the cPanel account to control your DNS, our Shared Web Hosting plans are provided specific URLs to use as nameservers. They will look something like this:
seans1.hostwindsdns.com
seans2.hostwindsdns.com
These would be the nameservers you provide to your registrar or the location in which you last paid for your domain. Once your domain is using these nameservers, your cPanel account takes control of the DNS records. You would edit them using the DNS Zone Editor within cPanel.
Cloud VPS Hosting DNS
The Cloud VPS hosting options provided at Hostwinds does not offer a default DNS manager. Not all clients need this. As such, Hostwinds provides an external tool within the Cloud Control portal. The Cloud DNS Manager acts as your DNS records manager. Nameservers that point to the Cloud DNS Manager look like this:
mdns1.hostwindsdns.com
mdns2.hostwindsdns.com
You will use these if you do not have a service or software running on your VPS that manages DNS records. Adding DNS records to the Cloud DNS Manager is a separate step and must be done manually in this case.
Private Nameservers
Whenever a nameserver is required, there is an option to create your own URL with a domain you own. For instance, if you own the domain example.com, you could create ns1.example.com and ns2.example.com.
DNS Wrap Up
Understanding the roles and functions of DNS is can be a difficult concept to grasp. Here at Hostwinds, our goal is to ensure you get the help you need. Don't forget that we are available 24/7/365 via LiveChat and through and technical support tickets, so if you have further questions, reach out!
Written by Hostwinds Team / June 5, 2021
