Hostwinds Blog
Search results for:
IMAP vs POP3: Key Differences and Ideal Uses
by: Hostwinds Team / January 25, 2024
IMAP and POP3 are client-side email protocols that dictate how email clients like Gmail, Outlook, and Apple Mail retrieve, store and organize emails received from the email server.
Both protocols share the common goal of retrieving emails. Why then are there two options?
What is IMAP?
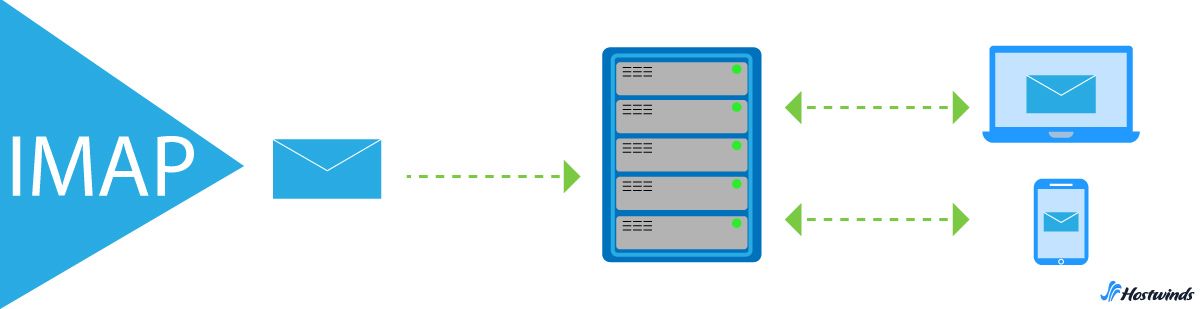
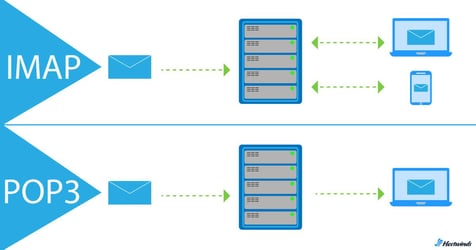
IMAP - Internet Message Access Protocol - is known as a two-way incoming message protocol. This means that actions performed by the email client (Gmail, Outlook, etc.) are reflected and stored by the email server, and vice versa.
For example, marking emails as read or moving them to a different folder on the client is synchronized with the server. Similarly, changes made on the server, like receiving new emails, are reflected on the client.
IMAP's two-way communication allows users to access and manage their emails from any device with an internet connection, while maintaining the original email client formatting.
What is POP3?
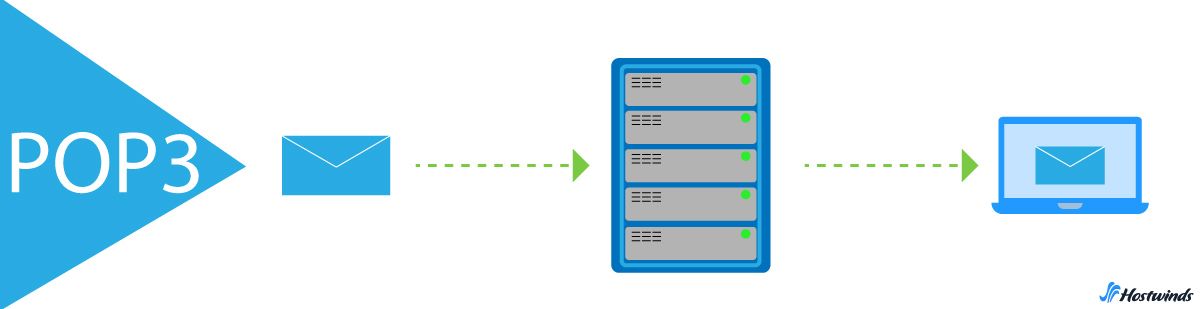
POP3 - Post Office Protocol Version 3 - is a one-way incoming message protocol, focusing solely on message retrieval. Unlike IMAP, after fetching a message from the server, the email client stores it on the device it was accessed from (phone, laptop, tablet) and ceases further communication with the server. In other words, it does not tell the server what it does with the email (marked as read, moved to folder, etc.)
Subsequently, the email is deleted from the server's database, making it available only on the accessing device. This means messages are not synchronized across devices; each device stores only the email it retrieved during its access to the client. This lack of synchronization also applies to outgoing emails.
IMAP vs POP3: Key Differences
IMAP and POP3 protocols share the common goal of email retrieval from a remote server. However, the manner in which they operate are quite distinct.
Here are a few key differences between IMAP and POP3:
| Feature | IMAP | POP3 |
| Client/Server Communication | IMAP supports two-way communication between the email client and server, allowing changes made on one to be reflected on the other. This includes actions like marking emails as read or moving them to folders. | POP3 is primarily a one-way communication protocol focused on retrieving emails from the server to the email client. It does not support two-way synchronization, meaning changes made on the client are not reflected on the server. |
| Message Retrieval and Storage | IMAP retrieves and displays email messages on demand, making it more bandwidth-efficient compared to downloading all messages at once. Emails are stored centrally on the email server rather than being downloaded to individual devices. | POP3 downloads entire emails from the server to the accessing device, storing them locally. Once downloaded, the original emails are typically deleted from the server, making them accessible only on the device where they were retrieved. |
| Folder Management | IMAP allows users to create and manage folders directly on the server. This ensures that folder structures are consistent across different devices, providing a more organized email experience. | Unlike IMAP, POP3 does not provide direct folder management on the server. Folders are typically created and managed locally on the email client, leading to potential inconsistencies across devices. |
| Email Access | IMAP is designed to facilitate access to emails from various devices. Changes made on one device, such as reading or deleting emails, are reflected across all devices connected to the same IMAP account. | POP3 is well-suited for users who prefer offline access to their emails. Since messages are downloaded and stored locally, users can access their emails even without an internet connection. |
| Security | IMAP provides a decent secure email communication environment. It supports encryption during data transmission, and can work in conjunction with secure protocols like SSL/TLS. However, users should ensure that their email provider implements proper security measures, regular software updates. | POP3 also offers fair security, but typically relies on encryption during the authentication process rather than the entire data transmission. Similar to IMAP, POP3 can utilize SSL/TLS to enhance security. However, it is considered less secure than IMAP in certain aspects, such as downloading emails to the local device, which may pose a higher risk if the device is compromised. |
Which Email Protocol Should You Use?
IMAP and POP3 are both viable email retrieval options but given their respective differences, individuals may prefer one over the other.
IMAP is ideal for users who frequently access their emails on multiple devices and desire a consistent mailbox experience. With two-way synchronization between the email client and server, users can enjoy enhanced organization and customization options. Storing everything on the remote server ensures real-time updates and alleviates concerns about potential email loss. It's also a great choice for those who prioritize collaboration and sharing mailbox access with others.
POP3 would be ideal for anyone planning to access their emails from a single device and would like to have those emails stored on the device. The simplicity of the one-way email retrieval protocol makes setup easy, and users can access their emails even without an internet connection. It caters to a straightforward and independent email access model, making it a suitable choice for certain use cases involving internet stability providing a sense of privacy as emails are stored locally on the device, reducing constant synchronization with a remote server.
Written by Hostwinds Team / January 25, 2024
